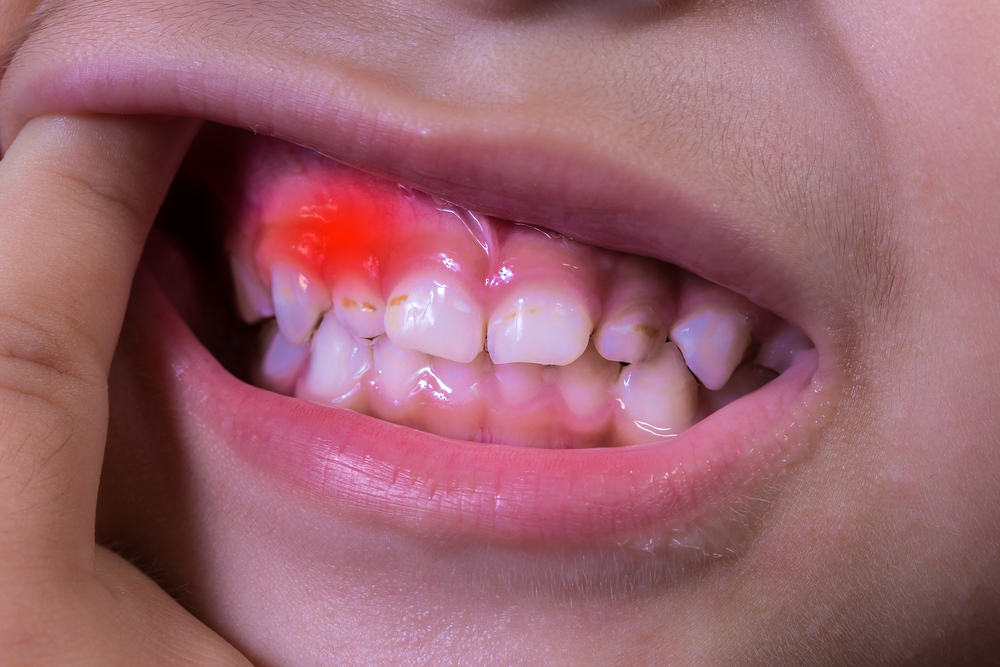
Causes of Gum Disease
One of the important and obvious causes of gum disease is the failure to perform a regular and correct brushing procedure. As a result, they are harmful residues called microbial dental plaque, which accumulates on the surfaces of the teeth, at the junction of the gums and between the teeth, in which there are many organisms. If these plaques are not cleaned, microorganisms and harmful substances that accumulate there cause tooth decay and gum disease. Since microbial dental plaque is the same color as the tooth, it is difficult to detect normally. Because the structure of plaque is soft, it can be easily removed from the surface of the tooth with the use of a toothbrush and dental floss. If it is diagnosed early and plaque is not cleaned, it calcifies and hardens and tartar forms. Its rough structure causes the plate to grow faster. In this way, it causes the formation of inflammation. Gum diseases cause the jawbones to melt due to inflammation. It can have serious consequences, from excessive infections that cause tooth loss. One of the causes of gum disease is swelling and bleeding of the gums. Bad breath occurs, and teeth move, open between them, and as a result can lead to tooth loss. One of the most important symptoms of gum disease is gingival bleeding, which is easily noticeable. It can occur when brushing teeth, eating hard foods, or on its own.
Treatment of Gum Diseases
The treatment of gum disease is called periodontal treatment. Gum diseases that occur in the soft and hard tissues surrounding the teeth are treated with different methods of treatment. The first treatment step is to clean the dental plaque formed in the teeth by the patient using a brush or dental floss, and the deposits on the teeth are cleaned by the dentist with special medical instruments. This stage is a treatment that is considered an initial treatment. Different techniques are used for simple gum inflammation or in advanced cases. If your inflamed gums have caused bone loss and there is a bone loss that prevents treatment, a bone transplant is performed in this area with the support of local anesthesia. Surgical procedures in which such surgical methods are used are called periodontal surgery. Periodontal surgery is a branch that concerns the gums and all the tissues surrounding the gums. It is a surgery for bone and tissue loss caused by inflammation. Gum is removed, inflamed tissues are cleaned, bone is corrected, and various biomaterials are used for new bone transplantation if necessary. The gum is then placed and sewn in place to cover the bone, and the tissue is left to heal. Stitches are removed in 1 -2 weeks. After surgery, doctor checks are required between 3-6 months. It is expected that the inflammation will disappear with treatment, the progression of the disease will stop and the formation of an oral environment in which the patient will perform effective cleaning on their own, and in the use of Biomaterials, the tissues that have been damaged as a result of the disease will be reconstructed. As a result of all this, the gums are naturally reconstructed and restore their former functionality.